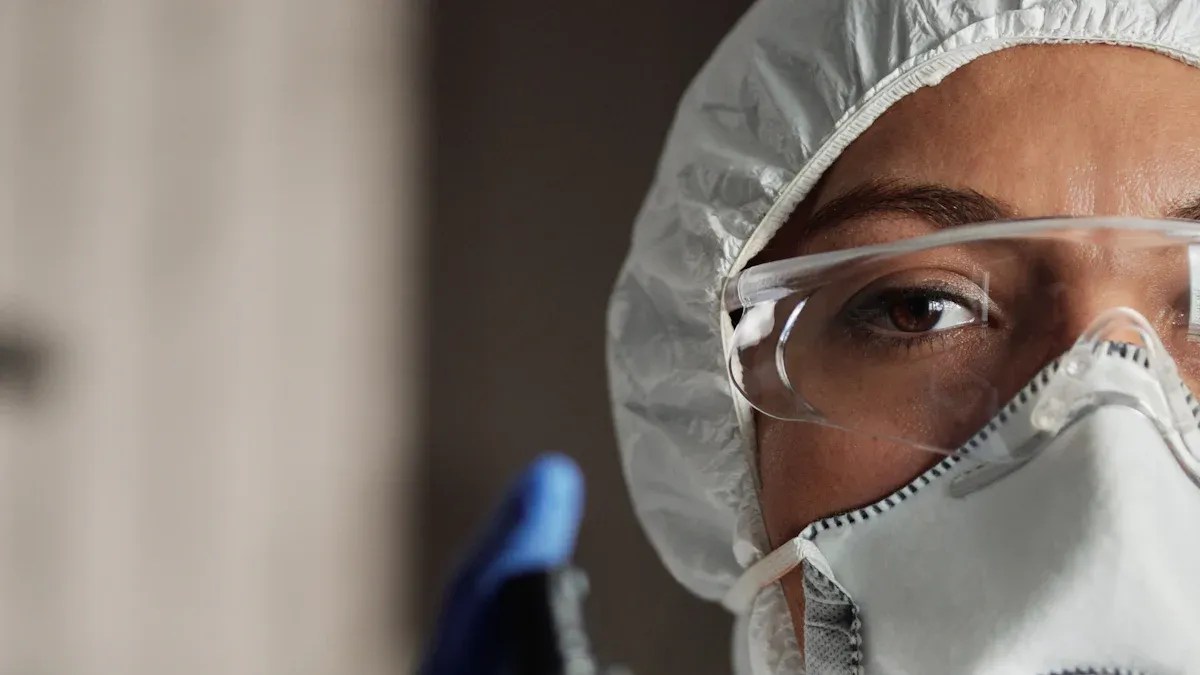
Building a Culture of Safety: Fulfilling USP 800 PPE Training Requirements is essential for creating a strong safety culture in your workplace. You must prioritize safety to protect your employees and ensure compliance with regulations. USP 800 PPE training plays a critical role in this process, as it empowers you and your team to understand the importance of personal protective equipment. When everyone is trained properly, they become more aware of their responsibilities. This awareness fosters a proactive approach to safety, which ultimately enhances the overall safety culture.
Key Takeaways
-
Prioritize safety in your workplace to protect employees and ensure compliance with regulations.
-
Implement USP 800 PPE training to empower your team and foster a proactive safety culture.
-
Regularly document and reassess training to maintain compliance and avoid administrative penalties.
-
Use proper PPE and follow donning and doffing techniques to minimize exposure to hazardous drugs.
-
Commit to continuous improvement in safety practices to enhance employee morale and patient care.
USP 800 Overview
USP 800, or US Pharmacopeial Convention Chapter 800, sets important standards for safely handling hazardous drugs in healthcare settings. This regulation aims to protect you and your coworkers from exposure to harmful substances. By following USP 800, you help create a safer work environment for everyone involved.
The relevance of USP 800 to safety cannot be overstated. Here are some key points about its impact:
-
Protects healthcare personnel: USP 800 ensures that those who handle hazardous drugs are safeguarded from potential health risks.
-
Ensures safe storage and transportation: The guidelines help maintain the integrity of hazardous drugs during storage and transport, reducing the chance of accidents.
-
Minimizes environmental contamination: By following these standards, you can help prevent harmful substances from affecting the environment.
-
Maintains compliance: Adhering to USP 800 helps you meet the requirements set by regulatory agencies like OSHA and NIOSH.
“USP 800 details proper planning and procedures for handling hazardous drugs including receiving, dispensing, compounding, administering, transporting, disposing, and cleaning to contain residues and prevent exposure.”
The impact of USP 800 on workplace safety is significant. Research shows that over 200 hazardous drugs can cause serious health effects due to occupational exposure. More than 100 studies have documented contamination in healthcare environments, highlighting the need for strict adherence to safety protocols. Additionally, over 50 studies indicate that hazardous drugs can be found in the urine of healthcare workers, confirming actual exposure risks.
By understanding and implementing USP 800, you contribute to a culture of safety that protects not only yourself but also your patients and the environment.
Key PPE Requirements for Safety

Types of Personal Protective Equipment
Under USP 800, specific types of personal protective equipment (PPE) are essential for safeguarding healthcare personnel from hazardous drugs. Here’s a list of the required PPE items:
-
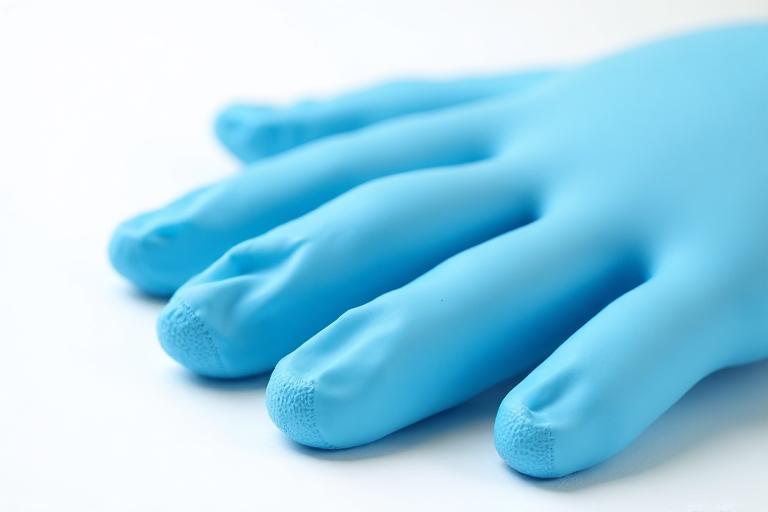
Gloves: Use chemotherapy gloves that meet ASTM D6978 standards. You should wear two pairs for added protection.
-
Gowns: Choose disposable gowns designed to resist permeability by hazardous drugs. Ensure they meet specific design requirements.
-
Head, Hair, Shoe, and Sleeve Covers: These items protect against hazardous drug residue. You need two pairs of shoe covers.
-
Eye and Face Protection: Goggles are necessary when there is a risk of spills or splashes of hazardous drugs.
-
Respiratory Protection: An N95 surgical respirator mask is required. Make sure to undergo fit-testing to ensure proper protection.
Proper Use of PPE
Using PPE correctly is crucial to minimize exposure risks. Follow these donning and doffing techniques to ensure safety:
-
Donning: Properly put on PPE to ensure full protection. Always follow the correct order:
-
Wear a gown for full body protection.
-
Put on a face mask for respiratory protection.
-
Use proper gloves for handling hazardous drugs.
-
Finally, wear goggles for eye protection.
-
Doffing: Carefully remove PPE to prevent self-contamination. Follow these steps:
-
Have an observer monitor your removal process.
-
Use designated zones (hot, warm, cold) for handling hazardous materials.
-
Always wash your hands before and after using PPE.
-
Dispose of PPE in designated waste containers.
-
Remember, improper donning and doffing can lead to occupational exposure. Common errors include lack of peer support and inadequate training for outpatient staff. Always ensure you have the right training and resources.
Disposal of Contaminated Materials
Disposing of contaminated PPE materials requires strict adherence to safety protocols. Personnel involved in cleaning and waste removal must be trained in proper procedures. This training ensures safety and environmental protection.
USP 800 does not govern waste disposal directly. Instead, it defers to existing federal, state, and local regulations for hazardous drug disposal. Always follow these regulations to ensure compliance.
By understanding and implementing these PPE requirements, you contribute significantly to a safer workplace. Proper use and disposal of PPE not only protect you but also your colleagues and the environment.
Building a Culture of Safety: Fulfilling USP 800 PPE Training Requirements

Training Techniques and Best Practices
To build a culture of safety, you must implement effective training techniques for USP 800 PPE compliance. Here are some systematic approaches that can enhance your training programs:
|
Recommended Strategies |
|
|---|---|
|
Training and competency |
* Identify areas where retraining is needed * Rewrite policies and procedures |
Engaging employees in training is crucial. Consider these best practices:
-
Utilize a healthcare-specific learning management system to provide tailored training courses.
-
Develop and implement comprehensive policies and procedures for handling hazardous drugs.
-
Ensure that Standard Operating Procedures (SOPs) are accessible to all staff for reference.
You should also focus on how to wear PPE properly and comfortably. Training should include information on PPE removal, especially after exposure to hazards. This knowledge empowers you to protect yourself and your colleagues effectively.
Documentation and Compliance
Documentation plays a vital role in ensuring compliance with USP 800 requirements. You must document training sessions and reassess them at least every 12 months. This reassessment should occur before introducing new hazardous drugs or significant changes in procedures.
Here are some key points to remember regarding documentation:
-
Personnel competency must be reassessed at least every 12 months.
-
Employees must receive training prior to the introduction of new equipment or a new hazardous drug.
Failing to document training can lead to serious consequences. Organizations may face administrative sanctions for not keeping accurate records. Non-compliance can result in fines and penalties from regulatory bodies.
|
Consequence Type |
Description |
|---|---|
|
Administrative Sanctions |
Organizations may face administrative sanctions for failing to document training. |
|
Regulatory Penalties |
Non-compliance can lead to fines and penalties from regulatory bodies. |
|
Increased Liability Exposure |
Organizations may experience heightened liability risks due to non-compliance with safety standards. |
For example, a pharmacy in California lost its sterile compounding permit due to non-compliance with USP <800>, which was linked to a compounding-related death. Such incidents highlight the importance of maintaining thorough documentation and compliance with safety standards.
By prioritizing training and documentation, you contribute to a robust safety program that protects health care workers and ensures compliance with regulations. This commitment to safety not only safeguards your team but also enhances the overall quality of care provided to patients.
Maintenance and Care of PPE
Best Practices for PPE Maintenance
Maintaining your personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial for ensuring safety in environments handling hazardous drugs. Regular maintenance routines and inspections help prevent common failures. Here are some best practices to follow:
-
Inspect PPE regularly: Check for any signs of wear or damage. Look for tears, punctures, or degradation in materials.
-
Store PPE properly: Keep PPE in a clean, dry area away from direct sunlight and contaminants. Ensure that it is easily accessible when needed.
-
Replace worn-out PPE: Do not use damaged equipment. Replace gloves, gowns, and other items that no longer provide adequate protection.
-
Follow manufacturer guidelines: Adhere to specific maintenance instructions provided by the PPE manufacturer to ensure optimal performance.
Common maintenance failures in USP 800 facilities include:
-
Use of improper PPE, particularly gowns and shoe covers, which do not provide adequate protection.
-
Reliance on general-use spun bound polypropylene gowns that lack proper particle control and barrier protection.
-
Substituting sterile surgical gloves for sterile cleanroom gloves, which can introduce contamination.
Emergency Procedures for Spills
In the event of a hazardous spill, you must act quickly and efficiently. Follow these steps to manage spills safely:
-
Ensure the use of appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE) such as:
-
HD gowns
-
Shoe covers
-
ASTM D6978 gloves
-
Fit tested N95 respirator
-
Eye protection (goggles or full facepiece respirator)
-
-
Prepare a spill kit containing:
-
Low-lint absorbent materials
-
Signage to notify of the spill
-
Container for hazardous waste disposal
-
Disposable scoop or shovel
-
-
Conduct spill drills regularly to familiarize staff with procedures:
-
Use mock spills for practice
-
Document the drills as part of training
-
-
Follow proper disposal procedures for spill contents:
-
Use a bag labeled for hazardous disposal
-
Consult with waste disposal companies for specific hazardous drug disposal methods.
-
Implementing these emergency procedures can lead to immediate containment and cleanup of spills by trained personnel. Ensure that your team is well-prepared to handle hazardous drug exposure effectively.
By prioritizing PPE maintenance and having clear emergency procedures, you contribute to a safer workplace and minimize risks associated with hazardous drug exposure.
Building a strong safety culture in your organization offers numerous benefits. It leads to improved employee morale, increased retention, and enhanced productivity. A positive safety culture reduces workplace incidents and fosters a sense of security among staff.
Ongoing USP 800 PPE training is vital for maintaining this culture. Regular training sessions keep your team informed about safety practices and exposure risks. They also ensure compliance with regulations.
Commit to continuous improvement in safety practices. This commitment not only protects your employees but also enhances the quality of care you provide to patients.
FAQ
What is USP 800?
USP 800 sets standards for safely handling hazardous drugs in healthcare settings. It aims to protect you and your coworkers from exposure to harmful substances.
Why is PPE important under USP 800?
Personal protective equipment (PPE) is crucial under USP 800 because it minimizes your risk of exposure to hazardous drugs. Proper use of PPE ensures your safety and compliance with regulations.
How often should I receive USP 800 training?
You should undergo USP 800 training at least once a year. Additionally, retraining is necessary when new hazardous drugs are introduced or when procedures change significantly.
What should I do if I spill hazardous drugs?
In case of a spill, immediately use appropriate PPE and follow your facility’s emergency procedures. Ensure you have a spill kit ready and conduct drills to prepare for such incidents.
How do I maintain my PPE?
Regularly inspect your PPE for damage and store it properly. Replace any worn-out items to ensure maximum protection while handling hazardous drugs.
Chemotherapy-tested gloves are the most frequently contacted PPE in hazardous drug handling. USP <800> mandates Double Gloving for all compounding and administration tasks. Medtecs N1000 Nitrile Series provides ASTM D6978 tested protection as the foundation of your hand protection protocol. Many facilities mistakenly use standard ASTM D6319 exam gloves for chemotherapy handling. This is non-compliant with USP <800>. Only gloves tested to ASTM D6978(chemotherapy-specific permeation standard at 35°C body temperature) are acceptable for antineoplastic drugs. Why N1000? Standard gloves fail as skin heats up. Medtecs N1000 series is tested at 35°C (Body Temperature Simulation) rather than standard room temp (23°C), ensuring the ASTM D6978 chemical barrier holds firm during real-world oncology operations. Micro-Textured Fingertip Pattern 4-5 mil Optimal Thickness Tested at 35°C (body temperature simulation) Highest permeation challenge High lipophilicity Common alkylating agent Nephrotoxic platinum compound Anthracycline cardiotoxin Taxane microtubule inhibitor Antimetabolite Folate antagonist Topoisomerase inhibitor Note: Carmustine and Thiotepa are the most challenging due to their small molecular size and high lipophilicity. > 30 min is the minimum ASTM D6978 requirement; Medtecs N1000 exceeds this threshold. Recommended chemotherapy gloves configuration for healthcare personnel Pro Tip: Using a larger size for the outer glove (e.g., inner M + outer L) reduces hand fatigue during extended compounding sessions—a practice endorsed by experienced oncology pharmacists. Choosing the Right Barrier Protection: Pharmacy Directors need a tiered approach. From pharmacy techs compounding daily to spill response teams handling waste containment systems—choose the right protection level based on drug categories and workflow requirements. Tier 1 Compounding Tier 2 Surgery/HIPEC Tier 3 Spill/Waste Oncology Pharmacists, Pharmacy Techs Engineered PPSB+PE Laminate: Moisture-Vapor Breathable Technology (MVTR) optimizes thermal comfort while maintaining full barrier protection against oral chemo and routine admixtures. Daily Admixture in C-SCA, Handling Oral Chemotherapy, Virtual Hybrid IV Certification. Under-and-Over Technique: Larger outer size reduces hand fatigue Surgeons, OR Nurses 63gsm Heavy Duty, AAMI Level 4, ASTM F1671 Viral Barrier. HIPEC Surgery, Trauma with Chemo Patients, High-fluid procedures. Under-and-Over Technique: Maintains sterile field + chemo protection EVS Staff, Spill Response Teams Type 5-B/6-B, Hooded, Taped Seams, Full body coverage. Compatible with Daniels' Sharpsmart protocols. Cytotoxic Drug Spills (>5ml), Waste Disposal, Disposing of HD. 100% Polyolefin material ensures Eco-Friendly Incineration (No toxic fumes). Under-and-Over Technique: Outer protects against sharps (broken glass)Main Oncology Solution:
Related USP 800 PPE Resources:
I. Compliance & Strategic Facility Management
II. Role-Specific Protection & Equipment Selection
The Definitive Guide to USP 800 PPE Compliance for Oncology Facilities
Essential Steps for USP 800 PPE Procurement
Mitigating Liability with USP 800 PPE Compliance
Essential Steps for Future-Proofing Your Oncology Facility with PPE Standards
The Business Case for Safety: Justifying Investment in USP 800 PPE
Global Perspectives on USP 800 PPE in Oncology
III. Operational Safety & Handling Protocols
Steps to Implement USP 800 Guidelines for Oncology Pharmacists
How to Effectively Implement USP 800 PPE Standards in Oncology Nursing
Advanced Protection: Choosing Chemotherapy Gowns and Gloves under USP 800
The Science of Safety: Choosing USP 800 PPE Fabrics
IV. Workforce Training & Safety Culture
Mastering USP 800 Guidelines for Safe Drug Handling
Optimizing Pharmacy Compounding Environments with USP 800 PPE
Master USP 800 PPE Strategies for Safe Spill Control
Mastering Environmental Safety with USP 800 Decontamination
Mastering Safe Disposal of Hazardous Waste in Healthcare
How to Ensure Effective Respiratory Protection Under USP 800 Standards
Integrating PPE and Engineering Controls for USP 800 Compliance
USP <800> Compliant Hand Protection Solutions
⚠️ Procurement Warning: Not All "Exam Gloves" Are Equal
Medtecs N1000 Series Specifications
Technical Specifications

Finger-Textured Design
Precision grip on glass vials and syringes without compromising the chemical barrier. Critical for Containment Aseptic Compounding Isolators where tactile feedback is essential.ASTM D6978 Breakthrough Times
Drug Breakthrough Status Carmustine > 30 min Pass Thiotepa > 30 min Pass Cyclophosphamide > 240 min Pass Cisplatin > 240 min Pass Doxorubicin > 240 min Pass Paclitaxel > 240 min Pass 5-Fluorouracil > 240 min Pass Methotrexate > 240 min Pass Etoposide > 240 min Pass USP <800> Double Gloving Protocol by Scenario
Scenario Inner Glove Outer Glove Change Frequency Sterile Compounding (USP <797>/<800>) N1000 (Chemotherapy-tested) under gown cuff ASTM D6978 compliant glove over cuff (sterile-ready options available) Every 30 min or immediately if compromised Non-Sterile Compounding N1000 (Size M) under gown cuff N1000 (Size L) over gown cuff Every 30 min or between patients Administration (Infusion Nurses) N1000 tucked under gown N1000 extending over gown cuff Between each patient Spill Response (>5ml) N1000 Nitrile (chemical barrier) Utility-grade Chemical Resistant Glove After spill cleanup complete Medtecs Solution Matrix: Tiered Protection for Every Role
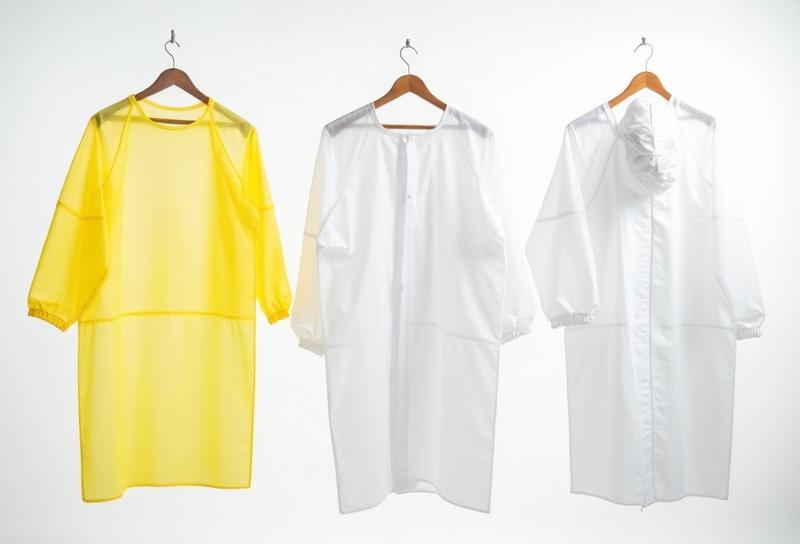

IL-4036YKTP (Yellow)
Specifications
Use Case
Key Features
Permeation Test Results*
🧤 The Perfect Pair: Gown + N1000 Gloves
IL-4063WKTP (White)
Specifications
Use Case
Key Features
Permeation Test Results*
🧤 The Perfect Pair: Gown + N1000 Gloves
IL-3063WEHTP (Coverall)
Specifications
Use Case
Key Features
Permeation Test Results*
🧤 The Perfect Pair: Gown + N1000 Gloves
Mandatory Add-ons (USP <800>)
Product Specification Comparison Table
Specification IL-4036YKTP IL-4063WKTP IL-3063WEHTP Product Type Isolation Gown Isolation Gown Coverall Weight (gsm) 36 63 63 Material PPSB+PE PPSB+PE SMS+PE AAMI Level Level 3 Level 4 N/A Permeation Resistance (19 drugs)* >480 min >480 min >480 min ASTM F1671 (Viral) — ✓ Pass ✓ Pass Type 5-B/6-B — — ✓ Yes Heat-Sealed Seams ✓ Yes ✓ Yes ✓ Yes Primary Use Case Compounding, Administration HIPEC, Surgery, Trauma Spill Control, Waste Disposal






